Latent Autoimmune Diabetes Of Adulthood
Though Latent Autoimmune Diabetes of Adulthood, sometimes abbreviated simply as LADA, is a rare form of the disease, the malady should still be taken quite seriously.
Causes
LADA is similar to the more commonly diagnosed Type 1 diabetes, which occurs because the body produces substances known as antibodies, which for some unknown reason attack the cells that produce insulin. These cells are situated inside the metabolic organ called the pancreas.
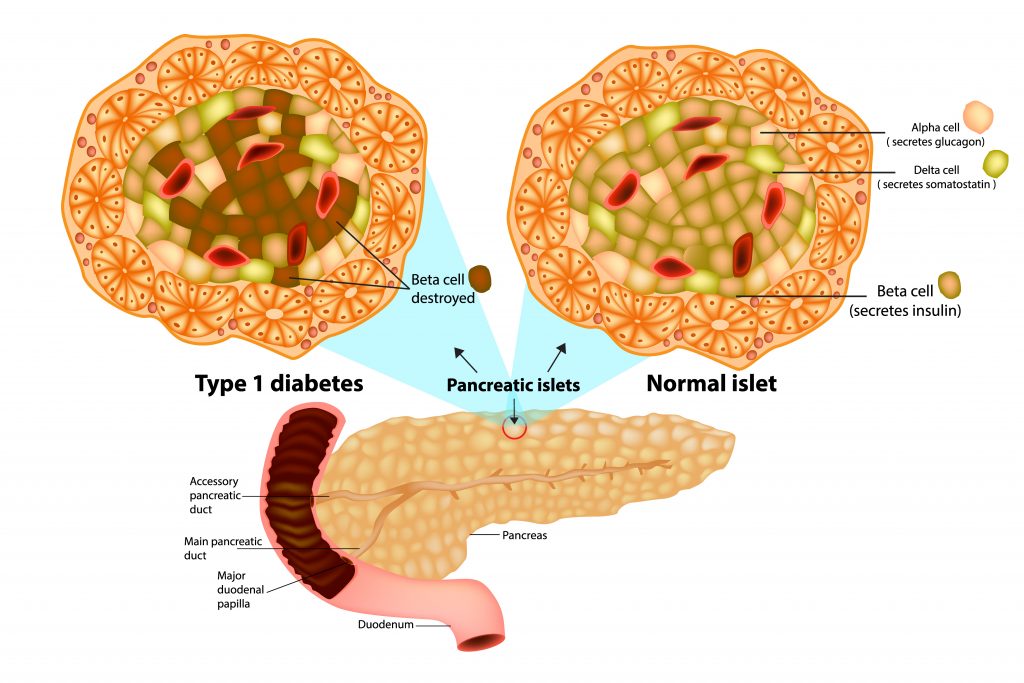
The hormone insulin is crucial to the body’s ability to regulate systemic concentrations of glucose, more commonly referred to as sugar. As antibodies eliminate insulin-producing cells, the pancreas simply cannot produce or secrete enough insulin to prevent glucose levels from spiraling out of control.
Symptoms
Physical manifestations of LADA often mimic other diabetic differentiations and include occurrences such as increased urinary output precipitating frequent trips to the bathroom, elevated hunger and thirst levels, vision issues, unexpected or unintended weight loss, skin maladies, increased infection risk, irritability, tiredness and nerve damage.
“Fortunately, those diagnosed with LADA experience a much slower progression of the illness”

There is one distinct difference, however, between LADA and its more common cousin, type I diabetes. Fortunately, those diagnosed with LADA experience a much slower progression of the illness than individuals stricken with the type 1 variation. Moreover, said individuals experience less harsher physical manifestations and are less likely to suffer potentially serious complications like heart and cardiovascular disease, kidney problems and serious systemic infections.
Diagnosis
Typically, LADA does not become symptomatic until after age 30. That said, there is only one effective method of confirming its presence, which involves the administration of a specific blood test determining the presence of insulin cell-damaging antibodies. Other tests that could augment the preceding examination include a procedure measuring bodily concentrations of C-peptide. This chemical is a protein that that often indicates how much insulin the body is producing.

Potential Treatment Options
As LADA is typically slow to progress, initial therapeutic protocols that often prove successful include the administration or oral medications. However, drugs must be supported by lifestyle habits such as:
Consuming A Healthy Diet

Those diagnosed with LADA are encouraged to consume foods like fruits, vegetables, grain products, fish and lean meats and avoid processed, canned and frozen products and those with high fat or sugar contents.
Maintaining A Normal Weight
Excessive weight can precipitate and definitely exacerbate diabetes symptoms. Keeping a healthy weight can be accomplished by eating well and obtaining adequate amounts of exercise.
Avoiding Detrimental Vices
Exorbitant alcohol intake and cigarette smoking are thought to worsen diabetic manifestations.
