Diabetes

Diabetes is a serious condition that has become a major health issue in the United States. The Center for Disease Control, or CDC, a nationally-based organization monitoring ailments impacting Americans and methods of controlling or eradicating said illnesses, conducted research in 2017 that concluded more than 30 million people are afflicted with this sickness. In more staggering terms, that equals more than nine percent of the country’s population. An additional seven million plus have the disease but have yet to be diagnosed.
“more than nine percent of the country’s population have diabetes!”
Diabetes Overview
The bodies of afflicted individuals do not properly metabolize the nutrient glucose, sometimes more commonly referred to as sugar. Typically, diabetics often experience elevated blood concentrations of glucose. When such spikes reach certain levels, the afflicted person could experience a number of untoward and potentially serious physical manifestations.
Causes
In many instances, stricken individuals possess an inability to properly produce and secrete a metabolic hormone called insulin. Insulin is paramount to normal sugar synthesis. The immune systems of certain diabetics attack insulin-producing cells, which are located inside an organ known as the pancreas. This lack of insulin ultimately precipitates a buildup of sugar that eventually collects in the bloodstream. Other diabetics cells grow resistant to insulin. As this resistance progresses, the pancreas experiences greater difficulty producing enough insulin to stabilize glucose levels this precipitating increased blood concentrations.
Risk Factors
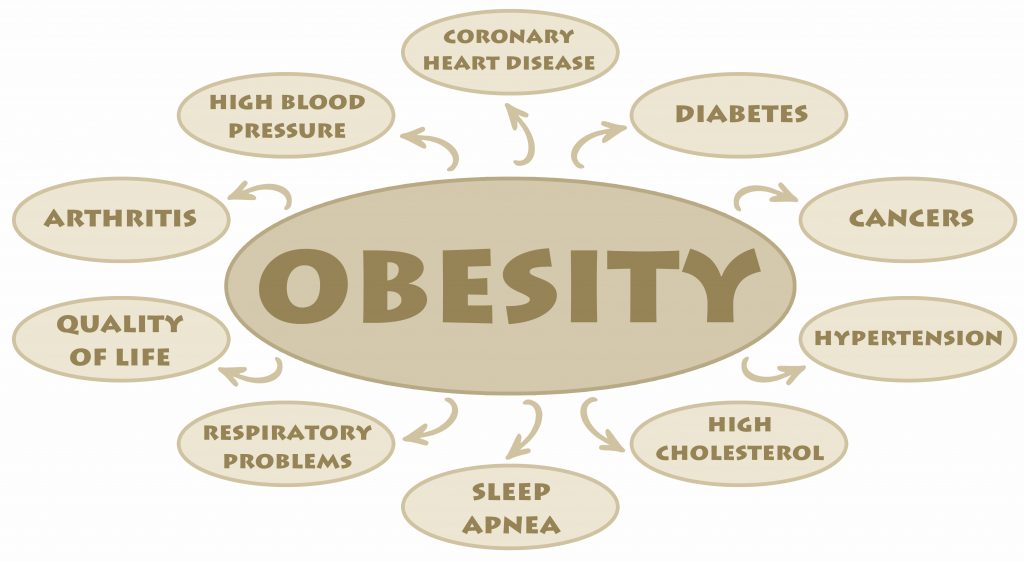
Several biological, environmental and lifestyle factors can increase one’s risk of developing the disease. Such issues include obesity, genetic mutations, family history, older age, leading a sedentary lifestyle, being of Hispanic, Native American, African American or Scandinavian heritage, various immune system disorders, exposure to certain environmental pollutants and ailments such as high blood pressure and elevated systemic concentrations of bad cholesterol.
Physical Manifestations
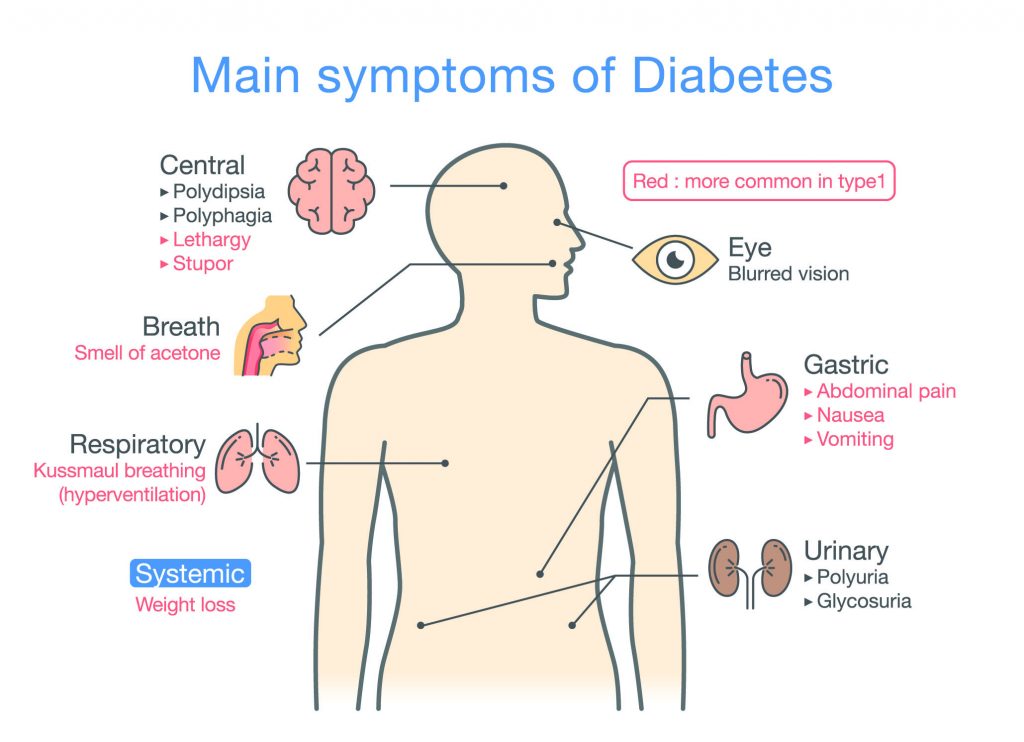
Diabetic symptoms can vary from person to person and be impacted by the condition’s severity. However, common manifestations include increased hunger and thirst, vision disturbances, elevated urinary output, weight loss, tiredness, repeated or chronic infections and delayed wound healing.
Complications
If not appropriately addressed, diabetes can wreak havoc on many systemic components and cause major health problems such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, vision issues, nerve damage and severe foot infections.
Diagnosis
Fortunately, the disease can be diagnosed following the administration of various blood tests such as the glycated hemoglobin test, random blood sugar test, the fasting blood sugar test and the oral glucose tolerance test.
Treatment Options
Physicians will employ therapeutic protocols based upon numerous factors such as the patient’s age, general health, specific type of diabetes and said malady’s severity. That said, routinely used remedial endeavors include medications and the administration of insulin. That said, for certain people, employing necessary lifestyle changes might precipitate a regulation in blood sugar levels. Said natural remedies include the consumption of a healthy, well-balanced diet, limiting alcohol consumption and obtaining proper exercise.
Prevention
In certain cases, diabetes prevention is not always plausible. However, the execution of certain simple tasks may increase one’s chances of preventing the contraction of said ailment. Such efforts include:
Maintaining A Healthy Weight
Few issues spike a person’s risk that being grossly overweight or obese. Eating less fattening foods and getting adequate exercise go a long way towards attaining and maintaining a healthy weight.

Avoid Being Sedentary
Exercise is paramount. However, avoiding a sedentary lifestyle means moving at all times. While strength training programs often prove valuable, simpler activities like walking burn calories, build muscle mass and maintain a healthy weight.
Limit Sugar And Fat Intake
Foods containing elevated concentrations of fat and sugar should be eliminated or significantly limited.
Quit Smoking
Cigarette smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing diabetes.
The Difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects the way that a person’s body regulates their blood sugar levels. According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC), over 100 million people who live in the United States currently struggle with the devastating effects that it has on the body. And that statistic is only in regards to the adults who have been diagnosed with it. Many children suffer from it too. But what some people may not know about diabetes is that there are two common types of it, and each type requires a special treatment plan to control it.
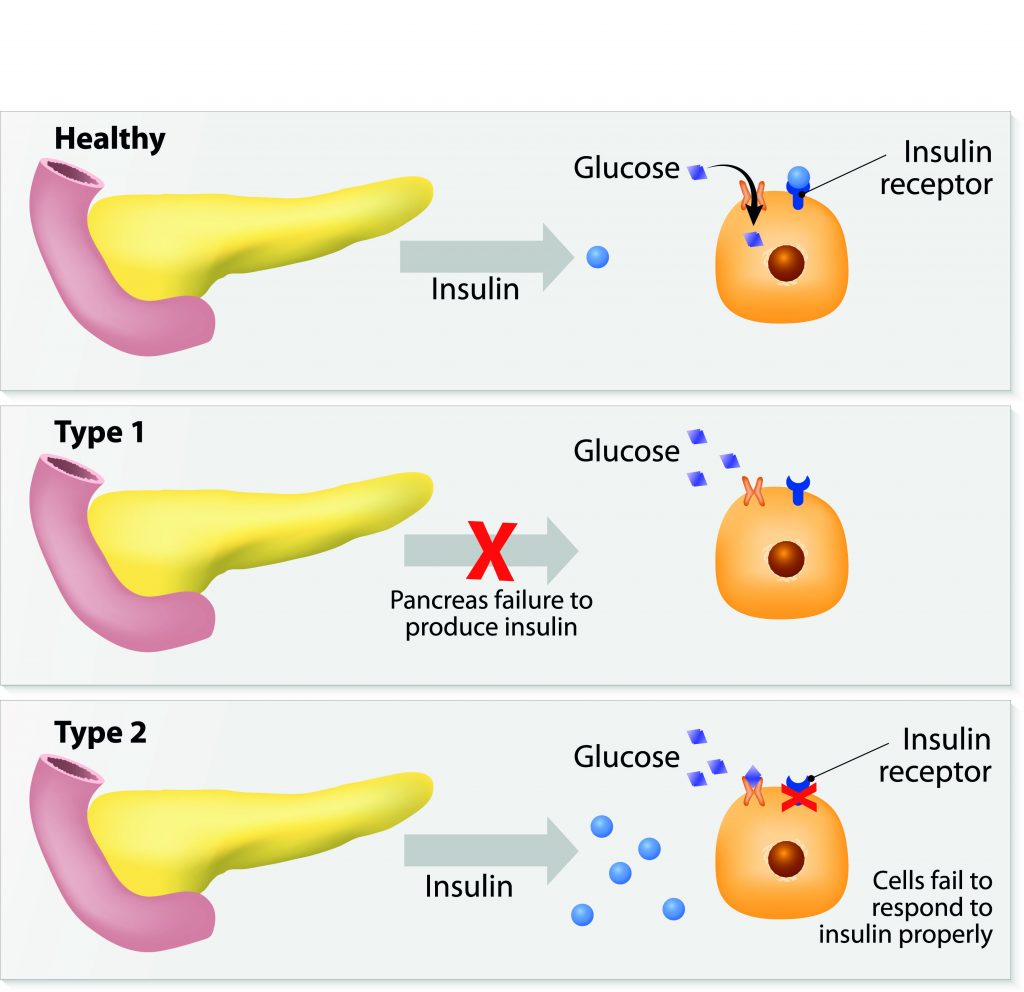
What is Type-One Diabetes?
Type-one diabetes is an autoimmune disorder wherein the body attacks the cells that are responsible for making insulin. Insulin is crucial to a person’s health because it acts as a key to open up the body’s cells, so they can receive sugar for energy. Without it, they begin to starve, and the sugar that a person gets from the food that they eat builds up in the blood stream. This causes it to reach extremely high levels very fast. Because of this, many people receive their initial diagnosis of type-one diabetes after a visit to an emergency room. Sometimes, this can be prevented if a person who knows that they have a family history of the condition gets tested regularly though.
What is Type-Two Diabetes?
Type-two diabetes is primarily caused by obesity and poor eating habits. It is different than type-one diabetes because a person who has this condition is often able to produce insulin, but their body doesn’t use it very well. This is often called “insulin resistance.” If a person is able to correct their weight by eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly, they can often reverse this condition.
How Are the Two Types of Diabetes Treated?
Because people with type-one diabetes don’t have enough insulin, they have to receive daily injections of it. And they may have to take other types of medications that lower their blood sugar levels along with them. Those who have type-two diabetes are primarily treated with medications, but they may need to receive insulin injections too if their condition becomes severe. Both type-one and type-two diabetes patients are encouraged to eat a healthy diet and exercise. And they have to monitor their blood sugar levels before and after they eat, shower in hot water, or perform any strenuous activity that could lower their blood sugar levels too much.
What is the Long-Term Prognosis for Both Types of Diabetes?
Although both types of diabetes are chronic conditions that last for years, they are both highly manageable. Any severe complications that occur from them are usually due to a patient’s struggle with eating a proper diet, exercising enough, and getting the medications or insulin injections that they need. Patients with type-one diabetes may struggle the most though because the insulin injections are done in the abdomen, and they can cause bruising and pain that is difficult to tolerate. Sometimes, they can cause weight gain too.
